DBSE Assessment Philosophy
Assessment is a continuous process of gathering evidence of student attainment of knowledge, understanding, skills and competencies. The primary aim of assessment and evaluation is to improve, enhance, and inform the teaching-learning process. Assessments at the Delhi Board of School Education (DBSE) are:
- Integrated into classroom learning for constant feedback and support
- Technology driven and scalable
- Based on real life contexts
- Competency based and student-centric
- Aimed to reduce teacher fatigue
Assessments are based upon best practices from around the globe. Students are reported on grades as marks are not representative of students’ ability and only reflects the amount of tasks completed by the student. Whereas, a grade description takes task difficulty into account and indicates student ability. A well-defined description of the grade achieved by the student can provide a reliable indicator of students' ability.
UNDERSTANDING DBSE ASSESSMENT
DBSE considers assessment as a part of learning rather than a separate process aimed at categorisation of students. At DBSE, assessments in the classroom are integrated with pedagogies and are based on competencies that students may require in future. Assessment inferences are reinforced by observations of the processes as well as the products of student learning activities. Students' responses to an assessment task are captured and analysed with sophisticated methodologies.
There are three types of assessments conducted at DBSE schools throughout a learning period:
- Assessment for learning: It is the process of gathering and interpreting evidence for use by students and teachers to know where the students are in their learning pathway, decide where they need to go and how best to get there. These assessments must always be accompanied by feedback and feed-forward mechanisms to enable deep learning. Example tasks include homework, classwork, class tests, assignments, projects, etc.
- Assessment of learning: It takes place at key points in the learning cycle, such as at the end of a learning period, to measure if students have achieved the learning objectives. Example tasks include exams, final projects, essays, etc.
- Assessment as learning: Students are provided with opportunities to monitor their own progress, self-assess and reflect on their learning. Example tasks include self-assessment, peer assessment, student portfulio, etc.
FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES FOLLOWED IN DBSE ASSESSMENTS
The fundamental principles ensure the validity and reliability of all DBSE assessments. The principles mentioned below inform all assessments at DBSE.
Assessments at DBSE are:
- fair, transparent and equitable
- supporting all learning needs of students
- set in relation to the curriculum expectation, learning goals, its outcomes
- aligned with the interests, learning styles, preferences, needs of all students to the extent possible
- communicated clearly to all the stakeholders involved at the beginning of the academic year and reinforced at other appropriate points throughout the year
- continuous and ongoing, diverse in nature, and administered over a period
- offering multiple opportunities for students to exhibit their full range of learning
- providing ongoing descriptive feedback, which is clear, specific, meaningful and timely to support improved learning and achievements
- designed to develop students’ self - assessment skills, set specific goals and plan next steps for their learning
In keeping with the assessment principle, DBSE uses assessment criteria to report a student's level of achievement in the respective subject area. This type of reporting enables students to:
- understand what they know and can do rather than being ranked against other students
- receive feedback based on their performance via level descriptors
- know beforehand what they need to do to achieve their learning goals
DBSE has adopted the grade-point system based on assessment criteria. The learning objectives in each subject are aligned with the assessment criteria. The criteria represent the use of knowledge, understanding, and skills taught in the subject.
STRUCTURE OF DBSE ASSESSMENTS
Global best practices suggest a multifaceted assessment structure. That is, students should be assessed in multiple ways and multiple times without increasing the workload of teachers or students.
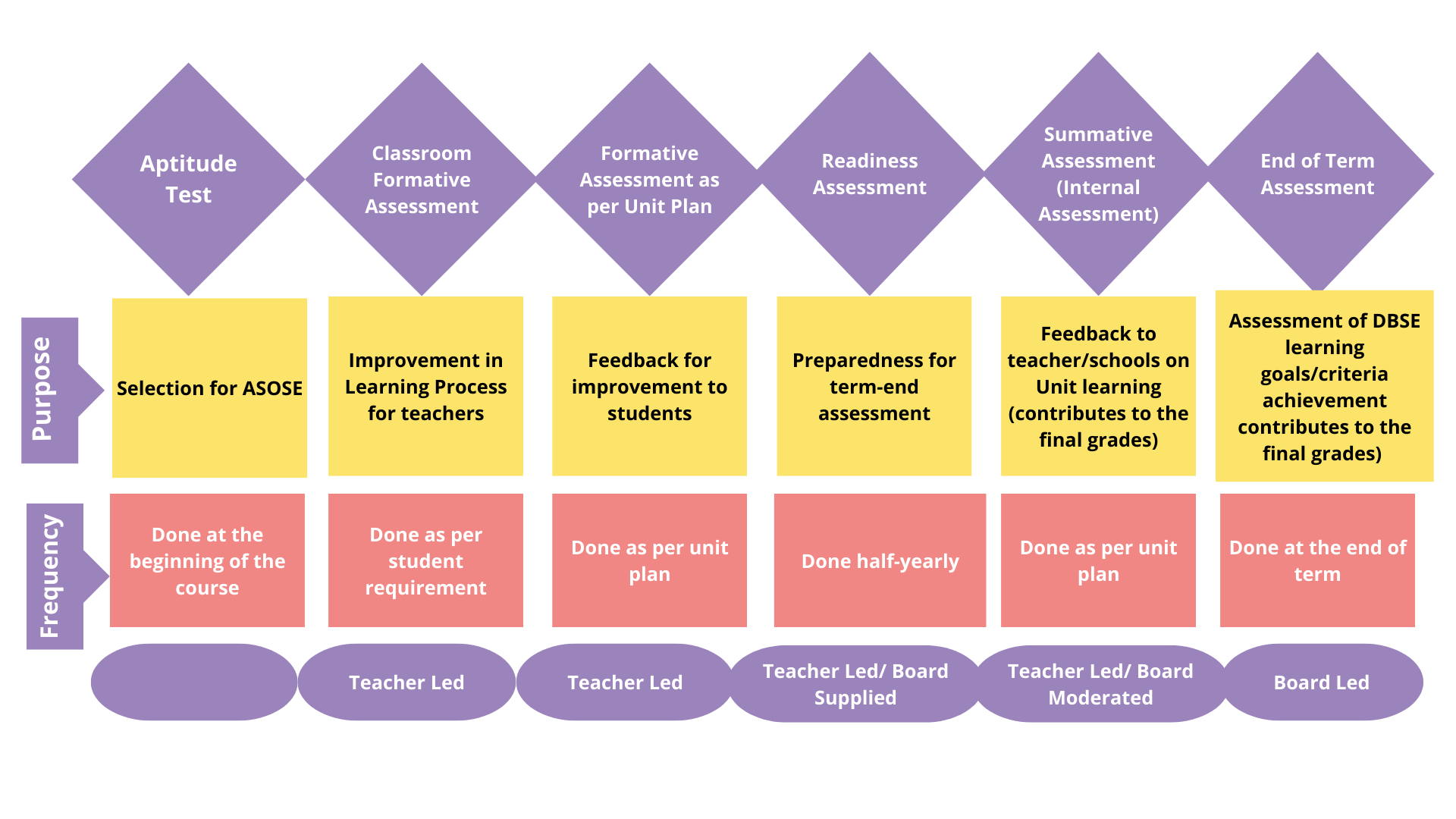
-
Placement/Aptitude Test
Students gain entry into DBSE secondary schools (ASoSEs) through a placement/aptitude test.
-
Classroom Formative Assessment
Classroom formative assessments are an integral part of the learning process. These are conducted as per teacher/student requirements. These assessments are developed by the teachers and administered by the teacher.
-
Formal unit-plan Formative Assessment
Formal unit-plan formative assessments are done to provide structured feedback for learning to students. These assessments are embedded in the structured unit plans and are developed by a group of expert teachers. Student performance in these assessments are not used for reporting, however, DBSE may monitor the usage of these assessments by teachers.
-
Readiness Assessment
Readiness assessments are done to provide exposure to term-end assessments. It provides an opportunity for the school/teacher/student to take corrective measures before the term-end assessment.
-
Summative Assessment (Internal Assessment/Unit end Assessments)
Internal summative assessment can be done at the end of each unit. They are recommended to be conducted through various assessment strategies and are not only limited to pen and paper assessments. Internal assessments will count towards student reporting.
-
Summative Assessment (External Assessment/Term-end Assessment)
External summative assessment is done at the end of each academic term. External assessments will count towards student reporting.
